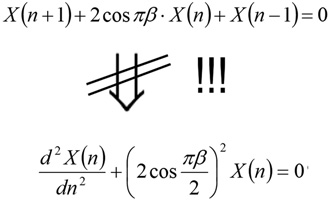Group identification of O-alkyl alkylphosphonothionofluoridates by electron ionization mass spectra on the basis of generalized spectral images of taxonomic groups
T14N3
Yu.I. Morozik, A.V. Dudkin, I.V. Ribal’chenk, A.R. Naumov
A method for group identification of poorly studied highly toxic O-alkyl alkylphosphonothionofluoridates by electron ionization mass spectra is proposed. The method is based on the use of generalized spectral images of four taxonomic groups of this class, subjected to control under the Convention on the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons. Generalized spectral images were found by analyzing the revealed regularities of fragmentation of these compounds. The advantage of the proposed method is that the assignment of the test substance to one of the class groups and to the class as a whole is a quick automated standard procedure used in the NIST information retrieval system.
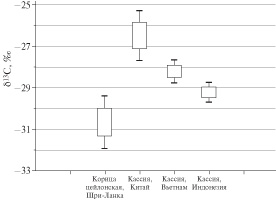
Authentification of plant culture Cinnamon by isotope ratio mass spectrometry
T14N3
Ju.B. Aksenova, I.V. Lapko, O.V. Kuznetsova, S.V. Vasilevsky,
A.V. Aksenov, V.F. Taranchenko, A.M. Antochin
Isotope compositions of nitrogen, carbon and oxygen in 69 different samples of cinnamon were determined by isotope ratio mass spectrometry. A discriminant model, allowing one to distinguish Ceylon cinnamon and cassia and to confirm the origin of cassia, has been proposed and tested. The accuracy of the discrimination was 95%. The results of this study can be used to prove the authenticity of cinnamon.
Products of intermediate oxidation of flavonoids in aqueous solutions and determination of their composition by high-performance liquid chromatography in combination with mass spectrometry
T14N3
V.V. Khasanov, K.A. Dychko, A. V. Labutin, S.S. Kravtsova, T.T. Kuryaeva
Using high-performance liquid chromatography in combination with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry [HPLC-MS-ESI(NEG)], quercetin [Q] and luteolin [L] oxidation intermediate products were investigated. It was established that in aqueous solutions at pH=8.0 under aerobic conditions, quercetin forms double and triple donor- acceptor type complexes of the {[Q][Q–H2]} and {[Q][Q–H2]2} composition, which can be separated by HPLC, but rapidly converted to deeper oxidation products. In the presence of another flavonoid, luteolin (L), the oxidized form of quercetin also forms mixed complexes of {[L][Q–H2]} and {[L][Q–H2]2} types. Luteolin during oxidation does not generate donor-acceptor {[L][L–H2]} complexes. Quercetin in complexes with luteolin is always present in an oxidized form. It can be assumed that these complexes are formed as a result of recombination of two radicals of flavonoids, which formed initially as a result of manifestation of the antioxidants properties (one-electron transfer). These transformations of flavonoids are possible if strict anaerobic conditions in their quantitative determination are not implemented.
Study of the products of oxidation of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine with nitrogen dioxide in aqueous solution by high resolution mass spectrometry
T14N3
N.V. Ul’yanovskii, D.S. Kosyakov, I.I. Pikovskoi, M.S. Popov
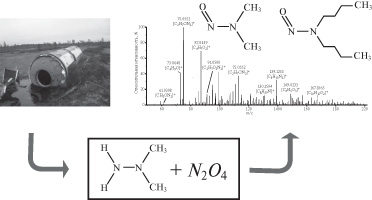
The products of interaction of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine with nitrogen dioxide in aqueous solution were characterized by high-resolution mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. It was found that more than 200 compounds of CHO, CHN and CHNO classes are formed as a result of the reaction; the main component being extremely dangerous N-nitrosodimethylamine. Among the products of the transformation of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, N-nitrosodibutylamine was identified for the first time. The obtained results are of importance for understanding the processes of transformation of rocket fuel in surface and ground waters in the places of falling spent rocket stages containing both propellant and oxidizer.
On methodological problems in the replacement of discrete mass spectrometric models with continual models
T14N3
A.S. Berdnikov, A.N. Verentchikov, N.V. Konenkov
Two problems that are significant for mass spectrometry (namely, the model of chemical kinetics of formation of clusters and the model of the pseudopotential of stroboscopic samples of coordinates and ion velocities in quadrupole radio-frequency fields) are considered as the examples to investigate the relationship between discrete models with finite-difference equations and continual models with point derivatives. In constructing continuum models, integer indices are replaced by real parameters, and finite-difference relations are replaced by approximate relations involving the derivatives. It is shown that this procedure is not safe: the discrete model and the continuum model can diverge globally contrary to the a priori intuitive considerations. As a result, the transfer of the conclusions obtained on the basis of the approximate continuum model to the exact physical model can lead to conceptually significant errors and requires the investigator to be careful. In particular, considered as an example the continuous model of chemical kinetics of formation of clusters and the continuous model of the pseudopotential of stroboscopic samples of coordinates and ion velocities in quadrupole radio-frequency fields are both insolvent.
Review. Mass Spectrometry of physiologically active substances prohibited in Sports: The problem of screening a wide range of compounds and their metabolites
T14N3
E.D. Virus, A.V. Ivanov, D.P. Luzyanin, A.A. Kubatiev
For the last 35 years, chromatography/mass spectrometry has been the main method of screening of physiologically active substances banned in sports. A characteristic feature of anti-doping control is the screening of a wide range of compounds with the applying of a large number of analytical procedures. This article introduces the reader to various approaches to the determination of physiologically active substances banned by World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) using mass spectrometry. The article describes various aspects of the anti-doping control and the criteria under which substances are caught in the WADA list. A detailed description of the pharmacological properties of certain classes of prohibited substances in the article should help to purposefully identify the potential “candidates” for WADA list. Considering the intensity of replenishment of the WADA list with “new” classes of prohibited substances and significant time and material costs associated with the implementation of a large number of analytical procedures in doping control, the need to find new approaches to screening a wide range of bioregulators in anti-doping control is emphasized.
T14N3
Contents