Isotopic analysis of highly enriched crystalline 28Si and initial 28SiF4 by high-resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
T15N3
P.A. Otopkova1, A.M. Potapov, A.I. Suchkov, A.D. Bulanov, A.Yu. Lashkov1, A.E. Kurganova
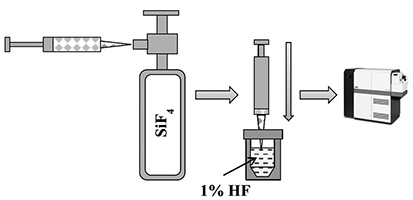
A technique for determining the isotopic composition of highly enriched silicon in the form of elementary 28Si and initial 28SiF4 by a single collector double focusing sector field ICP-MS over a wide range of isotope concentrations (more than 6 orders of magnitude) was described. To expand the range of measured isotopic concentrations the signals of the main and “impurity” isotopes were recorded in solutions of different concentrations. Determination of the matrix effects and the mass discrimination factors was carried out using the isotopic dilution method. This technique allowed us to realize the uncertainty of measuring the concentration of the main isotope to ten thousandths of a percent when enriching > 99.999% on a high-resolution single-collector mass spectrometer with inductively coupled plasma.
T15N3
Contents
The use of chemometric methods of data analysis for the identification and typification of petroleum and petroleum products
T15N3
T.A. Bolotnik, Yu.V. Timchenko, I.V. Plyushchenko, V.V. Levkina,
A.V. Pirogov, A.D. Smolenkov, M.V. Popik, O.A. Shpigun
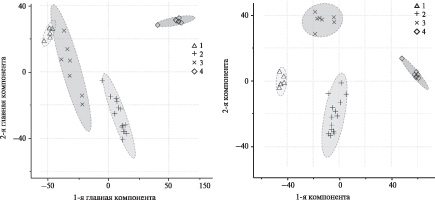
A method for identifying straits of rocket kerosene (RG-1 and T-1 brands) and various types of hydrocarbon fuels in the soil (aviation fuel ТС-1 and diesel fuel) has been developed. The proposed variant of identification is based on the preliminary separation of the main components by gas chromatography and their mass spectrometric detection, and processing of the obtained data with chemometric methods of analysis (principal component analysis and projection on latent structures with discriminant analysis) using the programs «MZmine2», «iMet-Q» and «MetaboAnalyst». The opportunity of application of the developed approach for the typification of saturated fractions of oils from different origins is illustrated.
Determination of phosphonylated tyrosine as a marker of exposure to nerve agents in blood plasma dry spots by HPLC-HRMS/MS
T15N3
N.L. Koryagina, T.I. Aliushina, G.V. Karakashev, E.I. Savel’eva, N.S. Khlebnikova, A.S. Radilov
A procedure for the determination of phosphonylated tyrosine, a marker of exposure to organophosphorus nerve agents, in blood plasma dry spot (DBS) samples by means of liquid chromatography/tandem high resolution mass spectrometry was developed. The DBS samples on Protein Saver 903 Card substrates were shown to be stable for 2 months on storage at 22 and 40 оС. It was found that the temperature of storage has a high impact on the stability of the DBS samples: the concentration of the analyte in the samples stored at 40 оС was about 3 times lower compared to the samples stored at room temperature. It was shown that the special Protein Saver 903 Card substrates could be replaced by an ordinary blue ribbon filter paper. In the latter case, the tyrosine adducts of nerve agents were reliably determined in the DBS samples stored for 1 month at room temperature (22 оС). However, for storage at elevated temperatures (40 оС), the use of filter paper substrates is not recommended. The proposed approach to storage of blood samples allows one to take and easily transport large series of samples and automate their analysis.
On the tryptic peptide features providing their detection and identification by MALDI mass spectrometry
T15N3
B.L. Milman1, А.V. Solov’eva, N.V. Lugovkina, I.K. Zhurkovich
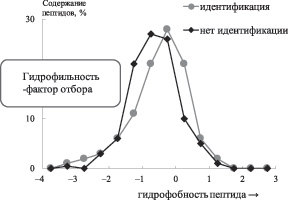
The tryptic peptide features providing detection and identification of these bio compounds and corresponding proteins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI) with the α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid matrix, are determined and discussed. Twenty five proteins were identified; the features of reliably identified peptides are compared to those of peptides which might be produced by tryptic cleavage and were not detected. Two key factors enhancing a detection possibility of tryptic peptides, were determined. The first one refers to the gas-phase peptide basicity, which is the highest for the C-terminal end arginine peptides; this reason for the emergence of big analytical signals is well-known. The second factor providing ionization of peptides under consideration in the MALDI conditions is their hydrophility. This result does not correlate with the most conclusions of earlier relevant researches and discussed in the article.
H3O+(H2O)n reagent ion. Calculation of the structure, thermodynamic parameters of hydration, equilibrium composition and mobility
T15N3
A.V. Lebedev
H3O+(H2O)n reagent ion is widely used in ion mobility spectrometry and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. In this work, the calculated data on the structure and properties of the H3O+(H2O)n (n = 0–4) reagent ion are obtained that are of interest for the study of the chemical ionization regularities, prediction and interpretation of ion mobility spectra and mass spectra. Using quantum chemical methods we computed the structure and refined isomeric composition of the H3O+(H2O)n ions. It is found that ions with n = 2, 3 and 4 have 2, 5 and 15 isomers respectively. The most stable isomers, which had a branched non-cyclic structure with the H3O+ core, are determined. The thermodynamic parameters of hydration reactions of the most stable isomers of H3O+(H2O)n (n = 0–3) and the equilibrium composition of the reagent ion in a wide range of temperatures and concentrations of water vapor are computed. The obtained results are consistent with the existing experimental and calculated data. Using the computed structural data and data on the composition of the reagent ion, its mobility is calculated by the trajectory method. The calculation error close to the experimental one is reached.
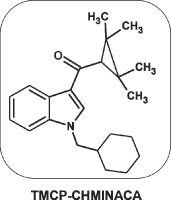
Detection of metabolites of TMCP-CHMINACA, the new psychoactive substance, in rat urine and serum by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
T15N3
E.V. Nikitin, A.M. Grigoryev, A.V. Labutin, S.E. Gribkova, I.A. Rodin, V.A. Kalashnikov, K.R. Ahmerov
The appearance of the new psychoactive substance TMCP-CHMINACA [3- (2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropane-1-oyl)-1-cyclohexylmethyl-1H-indole] on the market necessitated the determinftion of its chromatomass spectrometry characteristics as well as the search of its metabolites for further addition of their mass spectra to a library, used in screening of biological objects in forensic science. The structure of the molecule TMCP-CHMINACA has a significant similarity to the previously known synthetic cannabinoid TMCP-018 and TMCP-2201. High-resolution liquid chromatographic analysis of rats urine and blood serum after intravenous injection of the TMCP-CHMINACA solution showed metabolites that are the products of tetramethylcyclopropane residue carboxylation, N-dealkylation, and additional hydroxylyoxylation compounds of indole and tetramethylcyclopropane residues. Using chromatographic and mass spectrometry characteristics of TMCP-CHMINACA and its metabolites obtained from the study of rat biological fluids, a number of metabolites of both TMCP-CHMINACA and its isomer formed during smoking were found in urine studies of three people. At the same time, an unchanged TMCP-CHMINACA was detected on the surface and in the inner area of the hair sample of one of the participants. It has been established that an important way of biotransformation of TMCP-CHMINACA in both humans and rats is the carboxylation of the tetramethylcyclopropane residue combined with the monohydroxylation of the cyclohexylmethyl residue. For rats, the formation of N-dealkylation products combined with the monohydroxylation of the tetramethylcyclopropane residue is more typical. The presented mass spectra and retention characteristics of the detected metabolites can help in the detection of these (or similar) compounds in human biological objects.
Characterization of the structural forms of biomolecules based on the decomposition and separation of the charge state distributions of their ions
T15N3
V.V. Raznikov, M.O. Raznikova
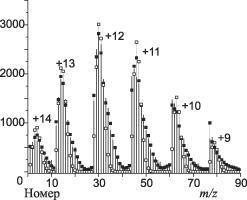
The aim of this work is the efficient disentangling and analysis of hidden information in mass spectrometric data on the structural composition of the studied solutions of biomolecules in their electrospray ionization. This paper provides a description of the algorithm of the sequential splitting combined with a decomposition of the measured charge state distributions of biomolecules, while increasing the number of individual components corresponding to the independent presence of charge carriers with the found probabilities of retention for a given number of ionogenic groups of these biomolecules. The article discusses the results of calculations for two-dimensional and one-dimensional decomposition of the charge distributions of cytochrome с with separation, presumably corresponding to different conformations of proteins. For the first time it was developed a method and tool for searching individual components and their contributions to the mass spectra of multiply charged ions, when the mass spectra of these components are not known in advance.