T16N1
Содержание
On the issue of informativeness of mass spectral diagnostic relations and criteria based on them for testing geochemical hypotheses
T16N1
M.B. Smirnov1, N.P. Fadeeva
Quantitative evaluation of the 1st and 2nd order errors for mass spectral criteria is obtained. These errors have been earlier suggested for distinguishing the oils generated in carbonate and other rocks for the Domanik formation of the northern and central regions of the Volga-Urals. It is shown that none of them work: the best mistakes of both the 1st and 2nd kind errors are close to 50%. Consequently, for all regions where carbonate oil source rocks are possible, a work similar to this should be done primarily, and only after that the analysis of oils becomes meaningful. In addition, it is necessary to conduct quantitative assessments of the quality of all the other criteria used in petroleum geochemistry for which such assessments are technically possible. New criteria should be designed only on the basis of those composition parameters for which the value of the Mann-Whitney criterion is close to zero.
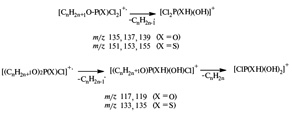
Gas chromatographic retention indices in GC/MS identification of alkyl dichlorophosphates, dialkyl chlorophosphates, and their thioanalogues
T16N1
I.G. Zenkevich, V.E. Nosova
Determining the set of analytical parameters for gas chromatographic/ mass spectrometric identification of reactive intermediate products of phosphoryl chloride (POCl3) and thiophosphoryl chrolide (PSCl3) interaction with aliphatic alcohols – O-alkyl dichlorophosphates (I), O,O-dialkyl chlorophosphates (II), O-alkyl dichlorothiophosphates (III), and O,O-dialkyl chlorothiophosphates (IV) is considered. The members of these series are not sufficiently presented in contemporary databases; the exception is the series (I) and (II), which are characterized with EI mass spectra (NIST MS Database, 2017) for 8 and 19 homologues, correspondingly. The set of data includes EI mass spectra and gas chromatographic retention indices (RI) on standard non-polar polydimethylsiloxane stationary phases. Strong differences in mass spectra of homologues of series (I) depending on conditions of their registration are revealed.
Comparing the RI values for alkyl chlorophosphates and -thiophosphates allows evaluating the increments for the hypothetic replacement of oxygen atom in the fragment P=O with sulfur atom (P=S), namely 59 ± 4 и 30 ± 4 for O-alkyl dichloro- and O,O-dialkyl chloroderivatives. Statistical processing of so-called homologous increments of retention indices leads to the average values attributed not to individual homologues, but to the homologous series. Using these values permits us evaluating the molecular weights of homologues containing no reliably detected signals of molecular ions in EI mass spectra.
Study of the nettle (Urtica diоica) lignin by orbitrap mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure photoionization
T16N1
I.I. Pikovskoi, D.S. Kosyakov, I.S. Shavrina, N.V. Ul’yanovskii
The orbital ion trap high-resolution mass spectrometry method with atmospheric pressure acetone-doped photoionization was first used to characterize the structure of lignins of herbaceous plants using the example of nettle (Urtíca dióica) dioxane lignin. The obtained mass spectrum contains about 3,000 peaks of deprotonated molecules of lignin oligomers in the molecular mass range up to 1.6 kDa. The study of tandem mass spectra and the composition of monomers formed during the collision-induced dissociation of lignin macromolecules showed the special role of p-hydroxycinnamic acids in the formation of nettle lignin. Based on the results of tandem mass spectrometry, possible structures of nettle lignin oligomers, which are formed by the addition of guaiacyl- and syringylpropane units with their subsequent etherification with p-coumaric, ferulic and dihydroferulic acids, are proposed.
Fixed-charge generation derivatization for analysis of thiols by «soft» ionization mass spectrometry methods
T16N1
A.V. Kozlov, R.S. Borisov, V.G. Zaikin
A new method for the fixed-charge generation derivatization of thiols of different structures by reaction with haloalkanes and dibromides was suggested. It was shown that 1,4-dibromobutane and 1,2-xylylene dibromide are the most effective alkylating agents, that provided the formation of stable five-membered ring with a positively charged sulfur atom. Such cations are readily detected by electrospray ionization and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry methods. Sulfonium cations were further studied by tandem mass spectrometry using collision-induced dissociation (CID). Typical and specific directions of CID for cyclic cations formed from thiols of different structures were established. They can be used to identify and quantify the thiol analytes by the selected reaction monitoring method.
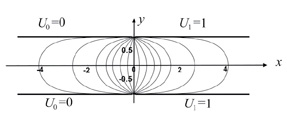
Analytical potentials for efficient simulation of planar and axisymmetric ion mirrors
T16N1
A.S. Berdnikov, A.N. Verentchikov, S.N. Kirillov, T.V. Pomozov, Yu.I. Khasin, M.I. Yavor
In the paper, analytical expressions for electrostatic fields of two-dimensional planar and axially symmetric mirrors with piecewise-constant and piecewise-linear potentials at electrode surfaces located symmetrically in parallel planes or on a cylindrical surface, in particular in presence of an additional cap electrode, are obtained. The results can be used for efficient optimization of aberration properties of time-of-flight mass analyzers and electrostatiс ion traps with gridless ion mirrors based on standard planar or ring-type electrodes with finite gaps between them, as well as on PCB plates.
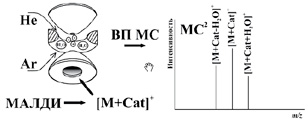
Quadrupole ion trap time-of-flight MALDI mass spectrometry: hydration of the ions of hydroxyl-containing compounds
T16N1
D.S. Kosyakov, O. Yu. Khoroshev, E.A. Anikeenko, N.V. Ul’yanovskii
On the example of a number of natural hydroxyl-containing compounds of various classes the possibility of artifact formation, associated with ion hydration, in the quadrupole ion trap MALDI mass spectra is shown for the first time. It was established that when using tandem mass spectrometry, both precursor ions and product ions are involved in the formation of water adducts. The main source of water for ion-molecular interactions in the ion trap are buffer and collision gases. The role of metal cations in the formation of analytes adducts with water is noted. For the majority of studied hydroxyl-containing compounds, hydration proceeds most actively during cationization with lithium ions, with the peak of the [M+H2O+Li]+ ion dominating in the mass spectra.
viQC: visual and intuitive quality control for mass spectrometry based proteome analysis
T16N1
E.M. Solovyeva, A.A. Lobas, A.K. Surin, L.I. Levitsky, V.A. Gorshkov, M.V. Gorshkov
Mass spectrometry-based bottom-up proteomics becomes a method of choice in a broad range of biomedical studies. However, because of the growing complexity of the mass spectrometers employed in these studies, there is an increasing need for robust and rapid quality control over the instrument performance. A variety of quality control tools targeting all aspects of LC-MS instrument operation have been developed recently. These tools are typically loaded heavily with a large number of metrics. Many of these metrics are difficult for interpretation for the regular users without extensive instrumentation and/or data processing experience. In this work, we introduced a set of simple and intuitively understandable metrics for assessing the quality of proteomic analysis, including the total experimental time and the number of spectral scans, ion accumulation time and intensity in both MS and MS/MS spectra, charge state distribution for precursor peptide ions, and the number of sequential MS/MS scans, etc. These metrics are implemented as an open-source utility, viQC, freely available at hg.theorchromo.ru/viQC. The developed tool has been tested experimentally using data from three different Orbitrap instruments and demonstrated its capability for assessing the possible flaws in the instrument’s operation and subsequent improving the efficiency of proteomic analysis.
Photocatalytic degradation of chlothianidin: effect of humic acids, nitrates and oxygen
T16N1
M.B. Kralj, E.G. Dilcan, G. Salihoğlu, D.M. Mazur, A.T. Lebedev, P. Trebše
The use of neonicotinoid insecticides has been constantly revised due to their impact on bees causing their decrease and bee malady. Unfortunately, because of the worldwide differences in pesticide regulation, chlothianidin is still allowed in European Union for greenhouse use and worldwide in some cases without any restictions. Lately, it was detected, on soil particles, in raw and drinking waters. The preparation of drinking waters implies different purification processes, including chlorination, ozonation, UV irradiation and nowadays advanced oxidation processes including TiO2. The TiO2 photocatalytic degradation of chlothianidin in the presence of oxygen, nitrate and humic acids was followed by kinetic studies, whereas the photoproducts formed were identified using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. The efficiency of different set-ups of photocatalytic degradation of chlothianidin was evaluated by identification of photoproducts and bioluminescence inhibition of bacteria Vibrio fischeri. The results indicated that the less harmful photoproducts are generated in the samples with added humic acids.