T13N3
Contents
Gas-phase fragmentation studies of biotinylated, hexaethylene glycol-spacered oligosaccharides — molecular probes — using electrospray mass spectrometry on hybrid high-resolution mass spectrometer
T13N3
A.O. Chizhov, D.A. Argunov, M.L. Gening, E.V. Sukhova, E.A. Khatuntseva, A.A. Karelin,
B.S. Komarova, M.V. Orekhova, V.B. Krylov, D.V. Yasunskii, Yu.E. Tsvetkov, N.E. Nifantiev
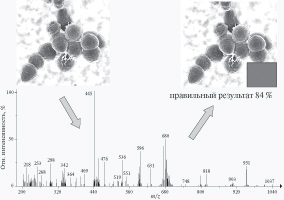
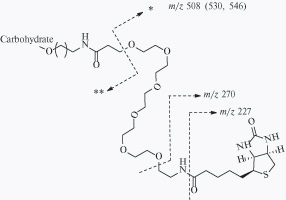
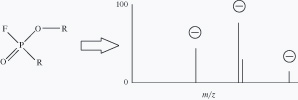
Electrospray ionization high-resolution mass spectra of biotinylated, hexaethylene glycol spacered molecular probes bearing biologically relevant carbohydrate moieties in positive and negative modes were recorded and interpret. Collisionally-induced decay mass spectra (positive mode) reveal different patterns depending on the charge of the parent ion, attached cations (or ions), the composition, and the sequence of carbohydrate fragment. The most intense peaks (two series) originate from the sequential cleavage of glycoside bonds resulting in charge location on the “reducing” end (Y series, observed for all compounds studied) or “non-reducing” end (B series). Fragmentation of the hexaethylene glycol chain giving rise to the cleavage of the C—O bond remoted from the biotin moiety is observed. Other fragment ions lighter than the mentioned above on the difference of (C2H4O)n were absent or much smaller. Similar fragmentation was found for all of the non-sulfated, biotinylated glycosides with the hexaethylene glycol spacer thus demonstrating that this type of fragmentation was characteristic for such molecular probes. Similar cleavages along with decay of biotin moiety via elimination of H2S and H2CS were observed for negative ions in collisionally-induced decay mass spectra of sulfated and neutral molecular probes.
Determination of the geographical region of growing the coffee beans by gas chromatograph-combustion – isotope ratio mass spectrometry
T13N3
A.M. Antokhin, V.F. Taranchenko, S.V. Vasilevsky, A.V. Aksenov, Ju.B. Aksenova, O.V. Kuznetsova,
I.V. Lapko, M.A. Glushkova
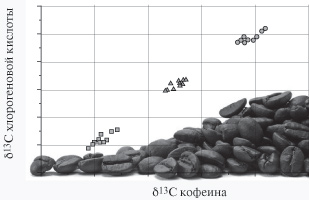
Gas chromatography –combustion –isotope ratio mass spectrometry has been used to study the changes in carbon isotopic composition of chlorogenic acid and caffeine extracted from samples of coffee beans of different origin. It has been shown that depending on the region of coffee beans growing, the relative characteristics of carbon isotopic composition, namely δ13C, ‰, changed significantly for both caffeine and chlorogenic acid. There was a decrease in the 13C isotope observed in the following order: Africa –South America –Central America. It has been found that the δ13C values for caffeine and chlorogenic acid, when mutually considered, provide the statistically significant identification of a region where the coffee beans grow.