T15N1
Table of contents
Electron ionization mass spectra of trimethylsilyl-pentafluoropropionyl and trimethylsilyl-heptafluorobutyryl derivatives of β-adrenoreceptor modulators
T15N1
A.A. Samosorova*, Yu.A. Efimova
The paper presents proposals for mass spectrometric determination of beta-adrenoreceptor modulators by bifunctional derivatization with N-methyl-N- (trimethylsilyl)-trifluoroacetamide followed by acylation with pentafluoropropionic or heptafluorobutyric anhydrides with a description of the derivatives obtained.
Resonant electron attachment to glucose and fructose molecules
T15N1
P.V. Shchukin, M.V. Muftakhov
Low-energy negative ion mass spectra of glucose and fructose suggest deep fragmentation of short-lived molecular ions. Analysis of metastable ions in the mass spectra shows that some decomposition reactions proceed through intermediate ions [M–H2O]– •, etc. Along with the general similarity of ionization processes in the isomers, there is a significant difference in the intensive formation of ions at m/z 71 from glucose.
Paradoxical secondary emission mass spectrum of the leuco form of methylene blue
T15N1
M.V. Kosevich, O.A. Boryak, V.S. Shelkovsky, V.G. Zobnina, V.V. Orlov
Paradoxical relation between secondary emission mass spectra of methylene blue dye and its leuco form is revealed: while the mass spectrum of the cation of the dye Cat+ (the oxidized form with m. w. 248 Da) reveals an abundant peak of the product of its reduction at m/z 285, the mass spectrum of its leuco form (the reduced form with m. w. 285 Da) corresponds to the oxidized form dominated by a peak at m/z 284. For the explanation to this experimental fact it is proposed that oxidation-reduction reactions induced by the ionization agents under secondary emission experiment conditions proceeds in the directions favourable for a given form of the redox-active compound , namely, an oxidized form undergoes reduction, whereas the reduced form is oxidized. Accounting this effect is required for correct identification of redox-active compounds basing on their secondary emission mass spectra, as well as for modelling of oxidation-reduction reactions in the systems containing redox-active dyes under the condition of mass spectrometric experiments.
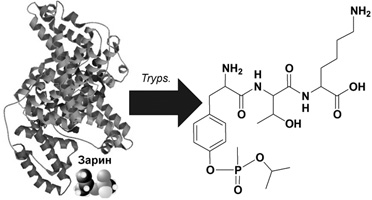
Selection of registration conditions and fragmentation study of peptide biomarker of sarin by high-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry
T15N1
A.N. Stavrianidi, A.V. Braun, E.A. Stekolshchikova, T.M. Baygildiev, I.A. Rodin, I.V. Rybalchenko
Identification of protein biomarkers of chemical warfare agents requires their reliable detection in the blood plasma at trace levels. This is a challenging task in the modern liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Existing approaches are based on the formation of tyrosine adducts with alkylmethylphosphonic acids after the cleavage of all proteins. The structure of such adducts is related to the type of chemical agent used. In this study, the possibility of detecting the tripeptide adduct of isopropylmethylphosphonic acid, obtained by trypsinolysis of the albumin adduct with sarin, in human plasma was shown. The study of the fragmentation ways of this analyte made it possible to identify the characteristic features of dissociation that can be used to determine other biomarkers of the application of chemical weapon. The conditions for recording the most intense ion transitions for rapid screening of blood plasma samples for the content of the albumin adduct of sarin with trypsinolysis according to the filter aided sample preparation method are described.
Synthesis of fringing magnetic fields for static mass analyzers of spectrographic type
T15N1
A.S. Berdnikov, L.N. Gall, A.S. Antonov, K.V. Soloviev
Static mass analyzers provide a unique potential opportunity to achieve 100% utilization of ions generated by a continuously operating ion source. However, to achieve this property it is necessary that the mass analyzer should operate not in spectrometric but in spectrographic mode. It is known that the classical Mattauch-Herzog scheme provides a spectrographic mode with double focusing (in angle and energy) along the straight focal line but of the first order only. The use of more complex optical solutions is prevented by the fringing fields of static magnets, which violate the exact spectrographic mode of operation of the instrument. The paper shows how, using the principle of the similarity of trajectories in Euler-homogeneous fields, it is possible to purposefully synthesize asymmetric fringing magnetic fields of a special type which keeps the spectrographic mode and the straightness of the focus line for static mass analyzers. Such fringing fields and fringing configurations of magnetic poles and screens can become the basis for static mass spectrographs of a new type with high optical characteristics.
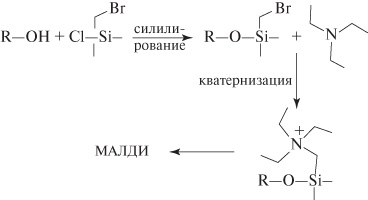
Silylation with the generation of a fixed charge for the analysis of alcohols by MALDI and SALDI mass spectrometry
T15N1
D.I. Zhilyaev, L.G. Voskresensky, N.Yu. Polovkov, R.S. Borisov
A new method of derivatization of alcohols for their analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) and surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization (SALDI) is proposed. The approach is based on the silylation of the analytes by bromomethylchlorodimethylsilane in the presence of tertiary amines to yield the fixed-charge containing derivatives. The proposed method was tested using aliphatic, terpenoid and steroid alcohols. MALDI and SALDI mass spectra of all derivatives contained intense ion peaks corresponding to their cationic parts.
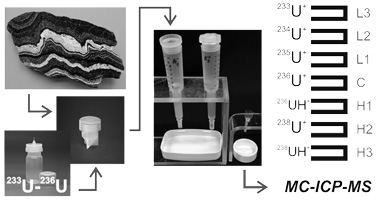
High-precision determination of 238U/235U isotope ratio in rocks by multicollector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
T15N1
G.V. Mandzhieva, A.S. Sadasyuk, I.V. Chernyshev, K.N. Shatagin, A.V. Chugaev, B.I. Gareev
The paper describes high-precision U-isotope analysis of rocks. The analysis is based on the multi-collector inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry (MC-ICP-MS) and includes, as an essential part, a three-stage ion-exchange chromatography uranium separation from chemically complex solutions. In the analysis, the 235U and 238U mass-bias of the MC-ICP-MS is corrected against the reference ratio of 233U and 236U in a double-spike added. The double-spiking precedes sample chemical digestion. This approach is useful as it corrects isotope data for a possible U-isotope fractionation that could have occurred during chemical preparation of samples. The double-spike 236U/233U is 1.03183 ± 0.00005. The extraction procedure allows more than 80% uranium yield. Accuracy of the analysis was estimated by the study of 238U/235U in international standard sample IRMM-3184 as well as in monitor samples. The uncertainty is estimated to be ± 0.008% (2SD) which is comparable to the accuracy of the results previously published by foreign researches.The analysis was elaborated for studying natural 238U/235U ratio variations. It is used by the authors for high-precision U-isotope composition determination in rocks (granites, shales, volcanic rocks) and U-bearing minerals.
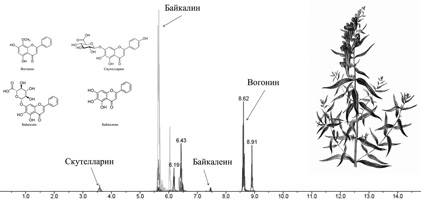
Simultaneous determination of wogonin, scutellarin, baicalin and baicalein in the extracts from Scutellariae baicalensis by high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry
T15N1
D.I. Baygildieva, T.M. Baygildiev, A.N. Stavrianidi, O.A. Shpigun, I.A. Rodin
Scutellariae baicalensis is one of the most popular herb in the traditional Chinese medicine. It is used for the treatment of inflammatory process, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and also in treatment of bacterial and virus infections due to such active components as wogonin, scutellarin, baicalin and baicalein that are contained in this herb. A sensitive and selective technique of simultaneous determination of these compounds in the extracts from plants raw materials using high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization was developed. The proposed method has been successfully tested on the commercially available samples of Scutellariae baicalensis root. Analysis of samples was carried out using a reversed-phase chromatography with Acclaim RSLC C18 sorbent. Using multiple reactions monitoring the following limits of detection were achieved: 1 ng mL–1 for wogonin and baicalin, 3 ng mL–1 for scutellarin and 4 ng mL–1 for baicalein. It was found that calibration curve was linear in the concentration range of 20 ng mL–1 and 2000 ng mL–1 for scutellarin and 20 ng mL–1 and 500 ng mL–1 for wogonin, baicalin and baicalein.