Determination of flavonoids of Epimedium by high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometric detection
T12N2
O.A. Shevlyakova, K.J. Vasil’yev, A.A. Ihalaynen, A.M. Antokhin,
V.F. Taranchenko, V.M. Goncharov, A.V. Aksenov, D.A. Mitrofanov,
I.A. Rodin, O.A. Shpigun
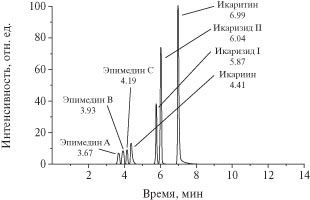
An approach for simultaneous detection of icariin, icaritin, icarisides I, II, epimedins A, B, C in extracts from plants and сommегсial pгoduсts was developed on the basis of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Using the dry and liquid extracts of Epimedium and the tea, the validation of the approach was carried out. Limits of detection were 5×10−4 mkg ml−1. For compounds determination, electrospray ionization in positive ion mode and tandem mass spectrometric detection in multiple reaction monitoring mode were used.
Mathematical elimination of spectral interferences at direct determination of rare earth elements in natural waters by inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry
T12N2
E.V. Elovskiy
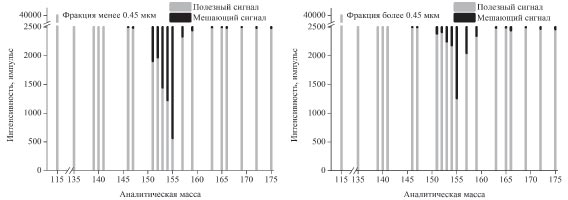
The paper gives original mathematical elimination models of oxide and hydroxide spectral interferences on analytical masses of rare earth elements for the quadrupole instrument in the mode oriented on the introduction of low-mineralized samples without the use of collision gas helium. Single model to eliminate spectral interferences with elements from La to Dy in the composition, as well as three models to eliminate spectral interferences with Ba in the composition were presented. A comparison of the efficiencies of the last three proposed models between themselves and with the previously used and described in the literature approach was given. Relative intensities of the oxide and hydroxide ions of elements from Ba to Dy were shown. For six river water samples from Primorye Territory (Russia) concentration of Ba and rare earth elements were obtained. They can be used for the correct interpretation of hydrogeochemical behavior of elements (especially Eu, Gd, and Tb). A method for calculating the integration time was presented.
Determination of nerve agent hydrolysis products in natural waters by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry
T12N2
I.A. Rodin, A.V. Braun, T.M. Baygildiev, I.A. Anan’eva, O.A. Shpigun, I.V. Rybalchenko
An approach to the determination of four nerve agents markers – S-(2-diethylaminoethyl) methylphosphonotioate, S-(2-diisopropylaminoethyl) methylphosphonotioate, bis (2-N,N-diethylaminoetil) disulfide and bis(2-N,N-diisopropylaminoethyl) disulfide – in aqueousenvironmental samples with the use of HPLC with tandem mass spectrometric detection was first developed. Optimal mass spectrometric detection and LC separation conditions were developed during the work. The proposed approach was applied to the analysis of real water samples and showed absence of matrix effect, good accuracy, reproducibility and selectivity. Detection limits achieved for S-(2-diethylaminoethyl) methylphosphonotioat, S-(2-diisopropylaminoethyl) methylphosphonotioat, bis(2-N,N-diethylaminoethyl) disulfide, and bis(2-N,N-diisopropylaminoethyl) disulfide in water samples were 0.0003, 0.003, 0.3 and 0.05 mg ml–1, respectively.
High-resolution time of flight mass spectrometry combined with high performance liquid chromatography for detection and determination of quinolones and sulfonamides in foods
T12N2
V.G. Amelin, A.I. Korotkov, N.M. Volkova
Method of high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with high performance liquid chromatography has been developed for the detection and determination of residues of 23 quinolones (fluoroquinolones) and a number of sulfonamides in foods. The samples were prepared using simplified and quick sample preparation. The limits of detection of quinolones and sulfonamides ranged from 0.05 (1) to 1000 (2000) mkg kg‒1. A scheme for identification and determination of detected quinolones has been developed using method of standard addition. The relative standard deviations of analysis results are less than 0.1.
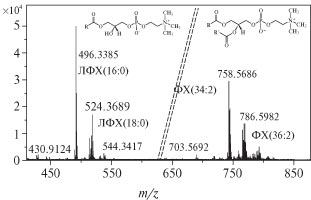
Comparative determination of fatty acid composition of low-molecular components of blood plasma by three mass spectrometry techniques: the ‘old-new’ exercise in lipidomics
T12N2
B.L. Milman, V.A. Utsal′, N.V. Lugovkina, I.A. Kotryakhov, I.K. Zhurkovich
Fatty acid composition of lipid low-molecular components of human blood plasma was determined by the combination of analytical techniques, such as gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and high-resolution electrospray MS1 and MS2 with direct flow injection. More than two tens of fatty acid methyl esters were identified in lipid extracts subjected to methanolysis. Direct injection electrospray MS led to recognition of 21 lysophosphatidylcholines and 25 phosphatidylcholine sum compositions. Fatty acid distributions over analytical signal intensities in groups of methyl esters and lysophosphatidylcholines were demonstrated to be similar to each other and highly correlated. The fatty acid distribution for phosphatidylcholine was correlated to those to a lesser extent. At the same time, the analytical signal intensities of lysophosphatidylcholines and phosphatidylcholine was observed to be highly correlated to concentrations of these lipid compounds in blood plasma determined by the similar technique of direct injection MS and available in the literature.
T12N2
Contents
|
B.L. Milman, V.A. Utsal, N.V. Lugovkina,
|
|
|
V.G. Amelin, A.I. Korotkov, N.M. Volkova
|
|
|
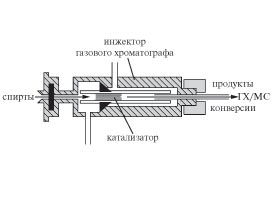
R.S. Borisov, N.A. Zhilyaeva, M.M. Ermilova,
|
|
|
I.A. Rodin, A.V. Braun, T.M. Baygildiev, I.A. Anan’eva, O.A. Shpigun, I.V. Rybalchenko
|
|
|
E.V. Elovskiy
|
|
|
O.A. Shevlyakova, K.J. Vasil’yev, A.A. Ihalaynen, A.M. Antokhin, V.F. Taranchenko, V.M. Goncharov,
|